what is a spectrometer used for|what does a spectrophotometer do : Brand manufacturer In the broadest sense a spectrometer is any instrument that is used to measure the variation of a physical characteristic over a given range; i.e. a spectrum. WEBA novela conta a história de Maria da Penha, Maria do rosário e Maria Aparecida, três domésticas que se aproximam para lutar por seus direitos e acabam formando o grupo musical Empreguetes.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webNovinha cavalgando ao som do funk. 30 sec Apollumsex -. Novinha cavalgando o pau com a buceta toda molhada. 2 min Proclamacaodarepublica -. 1080p. Enteada .
Strictly speaking, a spectrometer is any instrument used to view and analyze a range (or a spectrum) of a given characteristic for a substance (for example, a range of mass-to-charge values as in mass spectrometry), or a .Spectrometer, Device for detecting and analyzing wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, commonly used for molecular spectroscopy; more broadly, any of various instruments in . In the broadest sense a spectrometer is any instrument that is used to measure the variation of a physical characteristic over a given range; i.e. a spectrum.A spectrometer is an instrument that analyzes the light properties of an object or substance. It can measure the spectrum, mass, time-of-flight or magnetic properties of particles. Learn about its history, types, parts and applications .
Grating spectrometer schematic Internal structure of a grating spectrometer: Light comes from left side and diffracts on the upper middle reflective grating. The wavelength of light is then selected by the slit on the upper right corner. An .
Tungsten halogen, xenon lamps, and LEDs are usually used as light sources in a VIS spectrometer. It utilizes the same type of diffraction grating and detector as a UV spectrometer. The VIS spectrometer is also mainly .
A spectrometer is a widely-used scientific tool for many disciplines, including biology, chemistry, agriculture and more. There are several kinds of spectrometers, each type with far-reaching applications and unique strengths. Mass spectrometers measure the mass-to-charge ratio and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectrometers measure nuclear .
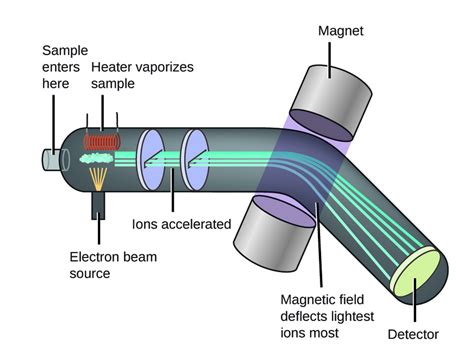
Most spectrometer designs use a single axis of dispersion - light is separated by wavelength only in one direction. When trying to measure very wide wavelength ranges, multiple diffraction orders can overlap. However, if a second dispersive element is added to the design these orders can be separated, creating a 2D “echellogram” that .Mass spectrometry is an analytical tool useful for measuring the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of one or more molecules present in a sample. These measurements can often be used to calculate the exact molecular weight of the sample components as well. Typically, mass spectrometers can be used to identify unknown compounds via molecular weight determination, to quantify .
A mass spectrometer is the instrument used to perform mass spectrometry. It works by ionizing chemical compounds to generate charged particles (ions) and separate them. The resulting data provides valuable information about the molecular structure and composition of the sample.EM radiation, including light, is a spectrum of different wavelengths. Spectroscopy is the detailed analysis of a light signal by wavelength. Ordinary color images break up light into 3 channels (red, green, and blue), but spectroscopy is generally concerned with breaking up light into a higher number of bands (e.g. 10, 100, or more), and a spectrometer is the instrument that does just .
An example of particle spectroscopy is a surface analysis technique known as electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) that measures the energy lost when low-energy electrons (typically 5–10 electron volts) collide with a surface.Occasionally, the colliding electron loses energy by exciting the surface; by measuring the electron’s energy loss, vibrational excitations .
A spectrophotometer, in general, consists of two devices; a spectrometer and a photometer. A spectrometer is a device that produces, typically disperses and measures light. A photometer indicates the photoelectric detector that measures the intensity of light. Spectrometer: It produces a desired range of wavelength of light. First a collimator . Differences between spectrometer and spectrophotometer. A spectrometer is a component of spectrophotometer used to measure different kinds of items. A spectrophotometer is a complete system consists of a light source that gathers light that interacted with the subject and the spectrometer for measurement. They differ in terms of usage.The Bendix spectrometer used by Gohlke and McLafferty was a “time-of-flight” instrument that produced a spectrum based on the time it took ions to traverse a long tube. Bendix began marketing a GC-MS device in 1959, but the first commercial success was LKB Instruments Inc.’s Model 9000, which debuted in 1965. The LKB instrument used a .
A spectrometer consists of several components A USB spectrometer is the most common type of spectrometer. They take light, separate it by wavelength and create a spectrum which shows the relative intensity of these separate wavelengths. Spectrometers have a wide range of applications and uses. Broadly speaking, all optical spectrometers consist . Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful qualitative and quantitative analytical technique used to identify and quantify a wide range of clinically relevant analytes.[1] When coupled with gas or liquid chromatographs, mass spectrometers allow the expansion of analytical capabilities to various clinical applications.[2] In addition, because of its ability to identify and . A spectrometer can separate the component colors coming either directly from an emission source or from the light transmitted through a sample. A top-down diagram of a spectrometer is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2: The light path through a simple spectrometer.
A spectrometer is any instrument used to probe a property of light as a function of its portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically its wavelength, frequency, or energy. The property being measured is usually intensity of light, but other . The spectrometer used in AAS can be either single-beam or double-beam. Single-beam spectrometers only require radiation that passes directly through the atomized sample, while double-beam spectrometers .An X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometer is an x-ray instrument used for routine, relatively non-destructive chemical analyses of rocks, minerals, sediments and fluids. It works on wavelength-dispersive spectroscopic . The spectrometer is an instrument that is used to measure and study the properties of light. It is also called a spectrograph or spectroscope.It is used to identify materials by studying the light emitted from or reflected from the materials. The spectrometer was invented by the German optical scientist Joseph Von Fraunhofer in 1814. Those spectrometers used a .
The process of tandem mass spectrometry provides information, thereby helping identify the protein. Use of Mass Spectrometers in protein identification: MS plays an important role in the identification of proteins. The two crucial protein identifications using MS comprise de novo sequencing and peptide mass fragmentation. A mass spectrometer is a device used to perform this measurement. The first mass spectrometer was built in 1912 by J.J. Thomson. Originally called a parabola spectrograph, the device was used to provide definitive evidence of nonradioactive isotopes. Through the years, the mass spectrometer has become one of the most useful devices found in . A spectrometer is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon (figure 1). The spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. A spectrograph — sometimes called a spectroscope or spectrometer — breaks the light from a single material into its component colors the way a prism splits white light into a rainbow. It records this spectrum, which allows scientists to analyze the light and discover properties of the material interacting with it. Spectroscopy is as crucial .
allow the use of intense light pulses to manipulate materials and molecules in unique ways, inducing phase transitions, ablating material, initiating nuclear fusion, and so on. . spectrometer, leave these items in an alternate location. The magnetic field can also .Raman spectroscopy can be used for microscopic analysis, with a spatial resolution in the order of 0.5-1 µm. Such analysis is possible using a Raman microscope. A Raman microscope couples a Raman spectrometer to a standard optical microscope, allowing high magnification visualization of a sample and Raman analysis with a microscopic laser spot.
To use a grinding wheel to remove dust and weathered rock, exposing fresh rock underneath. Location. Attached to the turret at the end of the rover arm. Mass. . Mössbauer Spectrometer calibration target was a thin slab of rock rich in magnetite mounted under the rover solar panels (it could also be used by the APXS). .
The type of analysis one wishes to do determines which type of spectrometer is used. Both dynamic and static SIMS usually use a magnetic sector mass analyzer because it has a high mass resolution. Static SIMS (as well as imaging SIMS) may also use a time-of-flight system, which allows for high transmission. .Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions.The results are presented as a mass spectrum, a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio.Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures.
ul325 cold impact test
Logon Portal de Apontamentos. Selecione o tipo de credenci.
what is a spectrometer used for|what does a spectrophotometer do